# GEMMA: Genome-wide Efficient Mixed Model Association
GEMMA is a software toolkit for fast application of linear mixed
models (LMMs) and related models to genome-wide association studies
(GWAS) and other large-scale data sets.
Check out [NEWS.md](NEWS.md) to see what's new in each GEMMA release.
Please post comments, feature requests or suspected bugs to
[Github issues](https://github.com/genetics-statistics/GEMMA/issues). We also
encourage contributions, for example, by forking the repository,
making your changes to the code, and issuing a pull request.
Currently, GEMMA is supported for 64-bit Mac OS X and Linux
platforms. *Windows is not currently supported.* If you are interested
in helping to make GEMMA available on Windows platforms (e.g., by
providing installation instructions for Windows, or by contributing
Windows binaries) please post a note in the
[Github issues](https://github.com/genetics-statistics/GEMMA/issues).
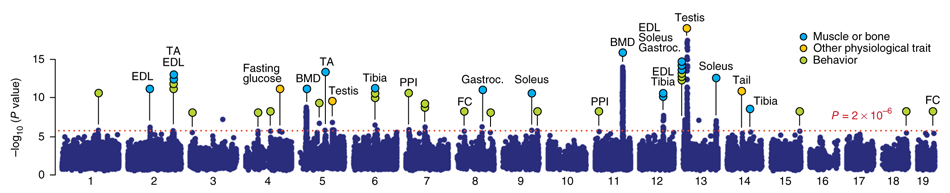
*(The above image depicts physiological and behavioral trait
loci identified in CFW mice using GEMMA, from [Parker et al, Nature
Genetics, 2016](https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3609).)*
## Key features
1. Fast assocation tests implemented using the univariate linear mixed
model (LMM). In GWAS, this can correct for population structure and
sample nonexchangeability. It also provides estimates of the
proportion of variance in phenotypes explained by available genotypes
(PVE), often called "chip heritability" or "SNP heritability".
2. Fast association tests for multiple phenotypes implemented using a
multivariate linear mixed model (mvLMM). In GWAS, this can correct for
populations tructure and sample nonexchangeability jointly in multiple
complex phenotypes.
3. Bayesian sparse linear mixed model (BSLMM) for estimating PVE,
phenotype prediction, and multi-marker modeling in GWAS.
4. Estimation of variance components ("chip heritability") partitioned
by different SNP functional categories from raw (individual-level)
data or summary data. For raw data, HE regression or the REML AI
algorithm can be used to estimate variance components when
individual-level data are available. For summary data, GEMMA uses the
MQS algorithm to estimate variance components.
## Quick start
1. Download and install the software. See [INSTALL.md](INSTALL.md).
2. Work through the demo. *Give more details here.*
3. Read the manual and run `gemma -h`. *Give more details here.*
## Citing GEMMA
If you use GEMMA for published work, please cite our paper:
+ Xiang Zhou and Matthew Stephens (2012). [Genome-wide efficient
mixed-model analysis for association studies.](http://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2310)
*Nature Genetics* **44**, 821–824.
If you use the multivariate linear mixed model (mvLMM) in your
research, please cite:
+ Xiang Zhou and Matthew Stephens (2014). [Efficient multivariate linear
mixed model algorithms for genome-wide association
studies.](http://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2848)
*Nature Methods* **11**, 407–409.
If you use the Bayesian sparse linear mixed model (BSLMM), please cite:
+ Xiang Zhou, Peter Carbonetto and Matthew Stephens (2013). [Polygenic
modeling with bayesian sparse linear mixed
models.](http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003264) *PLoS Genetics*
**9**, e1003264.
And if you use of the variance component estimation using summary
statistics, please cite:
+ Xiang Zhou (2016). [A unified framework for variance component
estimation with summary statistics in genome-wide association
studies.](https://doi.org/10.1101/042846) *Annals of Applied Statistics*, in press.
## License
Copyright (C) 2012–2017, Xiang Zhou.
The *GEMMA* source code repository is free software: you can
redistribute it under the terms of the
[GNU General Public License](http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html). All
the files in this project are part of *GEMMA*. This project is
distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but **without any
warranty**; without even the implied warranty of **merchantability or
fitness for a particular purpose**. See file [LICENSE](LICENSE) for
the full text of the license.
The source code for the
[shUnit2](https://github.com/genenetwork/shunit2) unit testing
framework, included in this repository [here](test/shunit2-2.0.3), is
distributed under the
[GNU Lesser General Public License](test/shunit2-2.0.3/doc/LGPL-2.1),
either version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later
revision.
## What's included
This is the current structure of the GEMMA source repository:
```
├── LICENSE
├── Makefile
├── NEWS.md
├── README.md
├── bin
├── doc
├── example
└── src
```
*Write a paragraph here briefly explaining what is in each of the
subfolders; see Wilson et al "Good Enough Practices" paper for example
of this.*
## Setup
To install GEMMA you can
1. Download the precompiled binaries (64-bit Linux and Mac only).
2. Use existing package managers, see [INSTALL.md](INSTALL.md).
3. Compile the GEMMA executable from source.
Compiling from source takes more work, but can boost performance of
the program, especially when using specialized C++ compilers and
numerical libraries.
Source code and [latest stable release][latest_release] are available
from the Github repository.
### Precompiled binaries
1. Go to the [latest stable release](latest_release) and download the
file appropriate for your platform: `gemma.linux.gz` for Linux, or
`gemma.macosx.gz` for Mac OS X.
2. Run `gunzip gemma.linux.gz` or `gunzip gemma.linux.gz` to
decompress the file.
3. For convenience, the binaries we provide are linked to static
versions of the GSL, LAPACK and BLAS libraries. So you do not need to
install these libraries.
4. Cince the program dynamically links to standard C++ and system
libraries, *you need to make sure that you have installed on your
system the same C++ compiler that was used to build the program.* For
example, `gemma.linux` was built using `gcc 4.8.5`, so you should have
`gcc 4.8.x`. If the libraries are installed somewhere non-standard,
you can tell where GEMMA can find the libraries by setting the
`LD_LIBRARY_PATH` environment variable. If you have the wrong version
of the C++ compiler, or if the libraries are in a place where GEMMA
cannot find them, then the program will complain about dynamic linking
errors.
### Building from source
*We provide a simple Makefile which will need to be customized; please
see the comments at the top of the Makefile. Explain why we
automatically generate a Makefile using programs such as CMake or
Autotools.*
You will need a standard C/C++ compiler such as GNU gcc, as well as
[GSL](http://www.gnu.org/s/gsl) and
[LAPACK](http://www.netlib.org/lapack) libraries. You will need to
change the library paths in the Makefile accordingly. *Note that GEMMA
currently does not work with GSL 2.x. We recommend linking to the
latest version of GSL 1.x, which is GSL 1.16 as of this writing.*
*Revise this step:* You will need to download the
[Eigen C++ library](http://eigen.tuxfamily.org), and copy the `Eigen`
subdirectory into the `src` directory of the GEMMA repository. (It was
last tested using Eigen version 3.3.3.)
More information on source code, dependencies and installation can be
found in [INSTALL.md](INSTALL.md).
## Credits
The *GEMMA* software was developed by:
[Xiang Zhou](http://www.xzlab.org)
Dept. of Biostatistics
University of Michigan
2012-2017
Peter Carbonetto, Tim Flutre, Matthew Stephens, Pjotr Prins and others
have also contributed to the development of this software.
[latest_release]: https://github.com/genetics-statistics/GEMMA/releases/tag/v0.96 "Most recent stable release"